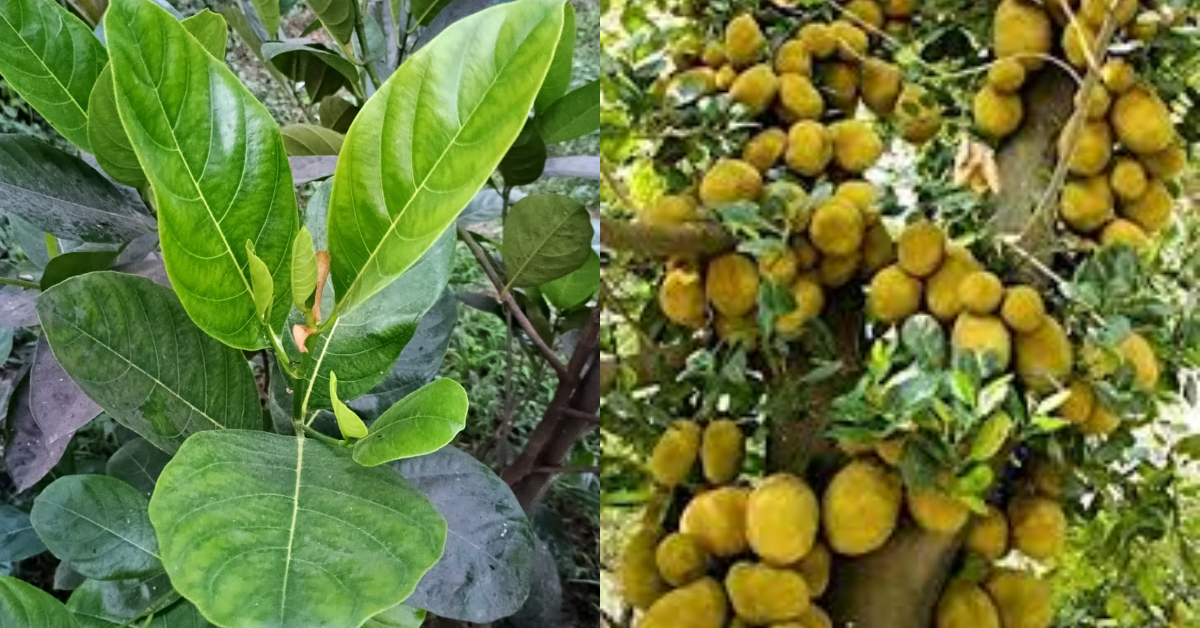

ഇതുകണ്ടാൽ നിങ്ങൾ ഉറപ്പായും ഞെട്ടും; ചക്ക നിറയെ കായ്ക്കാൻ ഇത് മാത്രം മതി; ഇങ്ങനെ ചെയ്താൽ ഇനി പ്ലാവിന് ചുറ്റും മതിയാവോളം ചക്ക ഉണ്ടാകും..! | Jackfruit Cultivation Tips
Jackfruit Cultivation Tips : കേരളത്തിന്റെ ഫല വൃക്ഷങ്ങളിൽ പ്രധാനിയാണ് പ്ലാവ്. പ്ലാവിൽ ചക്ക കായ്ച്ച് തുടങ്ങുന്ന സമയ മാണ് ഇപ്പോൾ. സാധാരണ താഴ്ഭാഗം മുതൽ മുകൾ ഭാഗം വരെ കായ്ക്കുന്ന ചക്ക ഇപ്പോൾ മുകൾ ഭാഗത്ത് മാത്രമാണു കായ്ക്കുന്നത്. ഇതിനാൽ മുറിച്ച് ഇടാനോ വെട്ടി എടുക്കാനോ പറ്റില്ല. അങ്ങനെ വരുമ്പോൾ ചക്ക ആർക്കും
ഉപയോഗിക്കാൻ പറ്റാത്ത രീതിയിൽ നശിച്ചു പോകാറാണ് പതിവ്. ഞാൻ ചക്ക താഴെ ഭാഗത്തായി കായ്ക്കാനും അതിന് എന്തൊക്കെയാണ് ചെയ്യേണ്ടതെന്നുമാണ് ഇന്ന് നമ്മൾ നോക്കുന്നത്. ചക്ക എന്നുള്ള പദത്തിൽ നിന്നാണ് ജാക്ക്ഫ്രൂട്ട് എന്ന ഇംഗ്ലീഷ് നാമം ഉണ്ടായത്. ലോകത്തെ വിവിധ ഫലങ്ങളിൽ ഏറ്റവും വലുതും ചക്കയാണ്. ക്യാൻസർ രോഗത്തെ വരെ പ്രതിരോധിക്കുന്ന
ഒരു ഔഷധഫലം കൂടിയാണ് ചക്ക അതുകൊണ്ട് തന്നെ ചക്കയ്ക്ക് ആഗോള തലത്തിലും നല്ല ഡിമാൻഡാണ്. പ്ലാവ് നന്നായി വളരാനും ചക്ക നന്നായി കായ്ക്കാനും സൂര്യപ്രകാശത്തിന്റെ പങ്ക് വളരെ വലുതാണ്. അതുകൊണ്ട് തന്നെ പ്ലാവ് എപ്പോഴും നല്ല സൂര്യപ്രകാശം ലഭിക്കുന്ന സ്ഥലത്ത് വേണം നടാൻ. മാത്രമല്ല വളർന്നു വരുന്ന പ്ലാവിനെ ആവശ്യമില്ലാത്ത ശിഖരങ്ങൾ
മുറിച്ചു കളയുന്നതിലൂടെ പ്ലാവിലേക്ക് സൂര്യപ്രകാശമേൽക്കുന്നത് കൂടുതലാകുകയും നന്നായി കായ്ഫലം കിട്ടാൻ സഹായിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യും. സാധാരണ ഗതിയിൽ പ്ലാവിന് വളപ്രയോഗം നടത്താറില്ല. കൂടുതൽ വീഡിയോയിൽ വിശദമായി നിങ്ങൾക്ക് കാണിച്ചു തരുന്നുണ്ട്. Video Credits : നമുക്കും കൃഷി ചെയ്യാം Namukkum Krishi Cheyyam
1. Climate and Soil Requirements
- Climate: Jackfruit thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. Optimal temperature: 25–35°C. It can tolerate short dry periods but is sensitive to frost.
- Rainfall: Requires 100–250 cm of annual rainfall. Good drainage is essential as waterlogging can kill the tree.
- Soil: Prefers deep, well-drained loamy soil. pH: 6.0–7.5. Avoid saline or heavy clay soils.
2. Variety Selection
- Local vs. Hybrid: Local varieties are hardy; hybrids often produce larger, sweeter fruits.
- Fruit Size & Type: Consider fruit size (large vs. medium) and taste (sweet vs. less fibrous) depending on market demand.
3. Propagation
- Seed Propagation: Seeds germinate well but may not retain the parent’s traits. Germination: 3–8 weeks.
- Vegetative Methods:
- Air layering: Produces true-to-type plants, takes 2–3 months.
- Grafting/budding: Best for uniform fruit quality.
4. Planting
- Spacing: 8–10 m between trees for proper canopy development.
- Planting Time: Start at the beginning of the rainy season.
- Pit Preparation:
- Size: 60×60×60 cm
- Fill with a mixture of topsoil, farmyard manure (FYM), and compost.
5. Watering
- Young plants need frequent watering, especially during dry spells.
- Mature trees tolerate some drought but require water during flowering and fruiting for good yield.
6. Fertilization
- Young Trees: Apply 500 g NPK (10:10:10) per tree annually, split into 2–3 doses.
- Mature Trees: 1–2 kg NPK per year; organic manure can be applied twice yearly.
- Micronutrients: Boron and zinc improve flowering and fruit set.
7. Pruning and Training
- Pruning: Helps maintain tree shape and improves sunlight penetration.
- Training: Remove weak branches; encourage a strong central leader for heavy fruit load.
8. Flowering and Fruiting
- Flowering Age: Seedlings: 3–8 years; grafted: 2–4 years.
- Pollination: Mostly insect-pollinated; bees improve fruit set.
- Fruit Development: 3–8 months depending on variety.
9. Pest and Disease Management
- Common Pests: Fruit flies, stem borers, mealybugs.
- Control: Trap fruits, use neem oil, remove infested fruits.
- Common Diseases:
- Rhizopus rot: Post-harvest; store in cool, dry places.
- Leaf spot: Fungicidal sprays (copper-based) can help.
10. Harvesting
- Signs of Ripeness: Fruit emits a strong aroma, skin changes color, sound becomes hollow when tapped.
- Method: Cut fruit carefully to avoid branch damage; use ropes for heavy fruits.
11. Yield
- A healthy mature jackfruit tree can produce 100–200 fruits per year depending on variety and care.
12. Tips for Commercial Success
- Select high-yield, disease-resistant varieties.
- Practice intercropping with short-duration crops during tree establishment.
- Ensure post-harvest handling and local market access to reduce losses.
Comments are closed.